Are you a product designer weighing material options for your next project? At Toolingsun, we work hand‑in‑hand with design teams to select the optimal steel grades, manufacturing methods, and surface finishes—ensuring your components meet performance, cost, and sustainability targets. In this blog, we’ll explore why steel remains a go‑to choice, outline the key alloy families, discuss processing techniques, surface treatment options, and share best practices for seamless collaboration between designers and manufacturers.
Why Steel Still Reigns Supreme in Product Design
Steel is essentially iron alloyed with carbon (0.02–2.1%), and—depending on the grade—with chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, and other elements. Designers value it for:
- Exceptional Strength & Durability: Tensile strengths from 300 MPa (mild carbon steel) up to 2,000 MPa (tool steels) support heavy‑load and safety‑critical applications.
- Formability & Toughness: Ductility and malleability allow deep drawing, bending, and forging into complex geometries without cracking.
- Cost‑Effectiveness: Compared to titanium or carbon‑fiber composites, steel delivers comparable mechanical performance at a fraction of the material cost.
- Recyclability & Sustainability: Virtually 100% of steel is recycled; using steel supports circular economy goals and often satisfies eco‑design mandates.
- Wide Availability: Global supply chains ensure consistent access to standard and specialty grades, keeping lead times short.
Whether you’re designing automotive structural parts, architectural hardware, consumer electronics housings, or medical device frames, steel provides the performance and versatility you need—at scale.
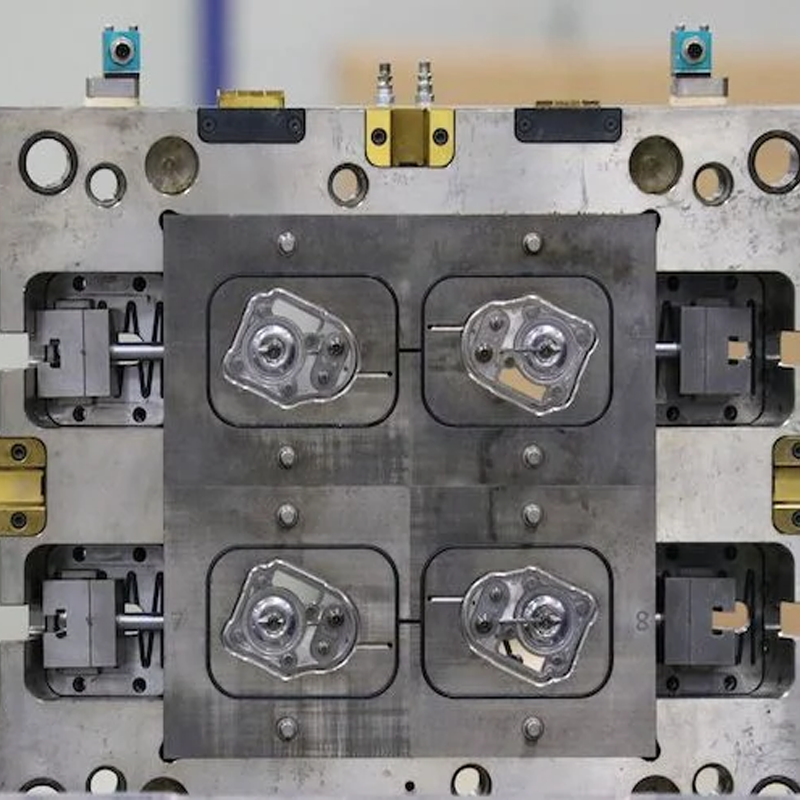
Key Steel Alloys Every Designer Should Know
1. Carbon Steels
Composition: Iron + 0.05–2% carbon; minimal alloying elements.
- Low‑Carbon (Mild) Steel (AISI 1010–1045): Good weldability and formability; tensile strength around 400 MPa. Ideal for chassis panels, brackets, and stamped parts.
- Medium‑Carbon Steel (AISI 1045–1050): Higher strength (~600 MPa) at the expense of some ductility; used for shafts, gears, and rollers.
- High‑Carbon Steel (> 0.8% C): Very hard and wear‑resistant; common in springs, saw blades, and cutting tools.
2. Alloy Steels
Enhanced Performance: Addition of Cr, Ni, Mo, V, etc., to achieve specific properties.
- Chromoly (e.g., 4140, 6150): Excellent fatigue resistance and toughness—used in aircraft landing gear and high‑stress shafts.
- Nickel‑Chromium Steels (e.g., 4340): High toughness at low temperatures; preferred for heavy machinery and high‑load fasteners.
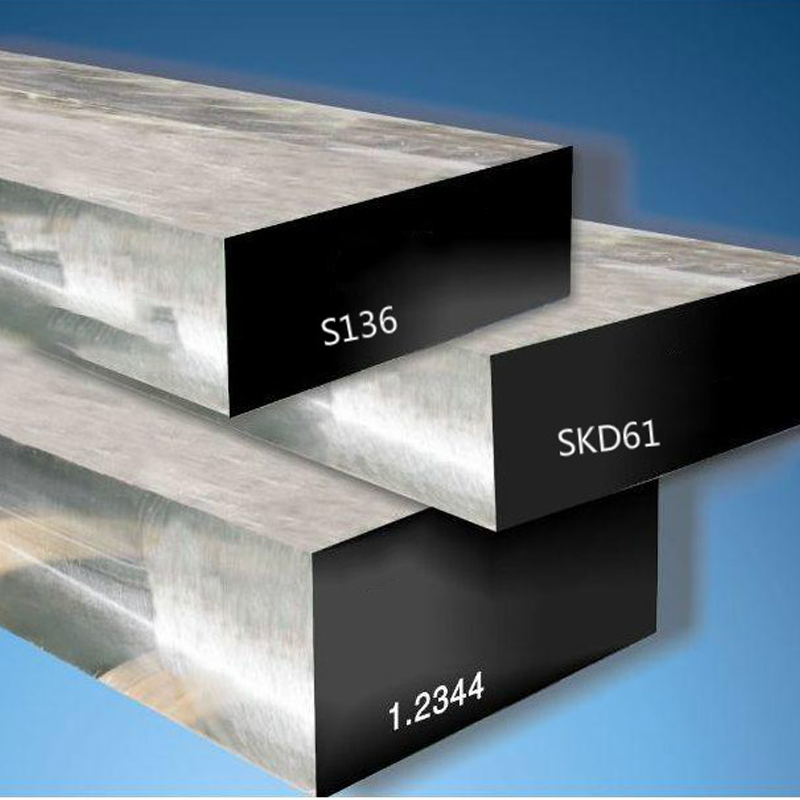
3. Stainless Steels
Corrosion Resistance: ≥ 10.5% chromium forms a protective oxide layer.
- Austenitic (304, 316): Non‑magnetic, excellent formability; used in food processing, medical instruments, and architectural trim.
- Ferritic (430): Magnetic, good corrosion resistance, moderate cost; suitable for automotive exhaust systems and decorative panels.
- Martensitic (410, 420): Heat‑treatable, high strength and hardness; found in cutlery, surgical tools, and valve components.
4. Tool Steels
Hardness & Wear Resistance: Enriched with tungsten, molybdenum, vanadium.
- High‑Speed Tool Steel (M2, M42): Retains hardness up to 600 °C; vital for cutting tools, drills, and broaches.
- D‑Series (D2, D3): High chromium content for exceptional abrasion resistance; used in dies, punches, and shear blades.
5. High‑Strength Low‑Alloy (HSLA) Steels
Strength‑to‑Weight Optimization: Yield strengths 350–700 MPa, high toughness.
- SAE1006–SAE1090 Series: Fine grain structure for improved formability; ideal for structural automotive components and chassis frames.
- Weathering Steels (e.g., Corten): Naturally develop a protective patina—used for outdoor architectural elements and cargo containers.

When to Look Beyond Steel
Despite its versatility, steel isn’t always the best choice:
- Weight‑Sensitive Applications: Aerospace, handheld electronics, and sports equipment may benefit from aluminum, magnesium, or composites.
- Extreme Corrosion Environments: Marine outboard motors or chemical processing equipment sometimes require titanium or exotic alloys.
- Ease of Prototyping: Rapid iteration with polymers, 3D‑printed plastics, or low‑temperature metals can be more efficient early in development.
Understanding these limitations helps product designers choose the right material from the start—minimizing costly changes later.
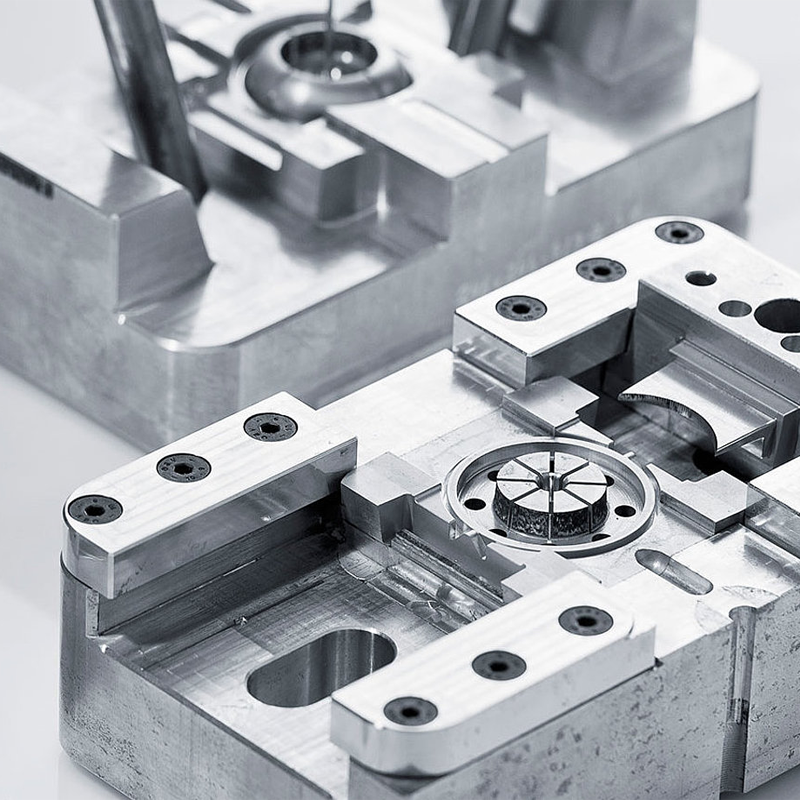
Steel Manufacturing Processes: Matching Material to Method
Casting
- Overview: Molten steel poured into sand or permanent molds.
- Advantages: Complex shapes and large parts with minimal machining.
- Considerations: Design for shrinkage (1–3%) and potential porosity.
Forging
- Overview: Steel deformed under high pressure, often at 1,100–1,300 °C.
- Advantages: Superior strength and fatigue life due to refined grain flow.
- Considerations: Requires robust dies; less geometric flexibility than casting or machining.
Machining
- Overview: Material removed via CNC milling, turning, and grinding.
- Advantages: Tight tolerances (±0.01 mm) and excellent surface finishes.
- Considerations: High tool wear on harder steels; longer cycle times.

Welding
- Overview: Joining steel components via MIG, TIG, or arc welding.
- Advantages: Strong, permanent joints; suitable for large assemblies.
- Considerations: Heat‑affected zones can alter microstructure; careful design of joint geometry.
Sheet Metal Forming
- Overview: Stamping, bending, deep drawing, and roll forming of sheet steel.
- Advantages: High production rates, consistent part geometry.
- Considerations: Springback management, minimum bend radii, and tooling costs.
Surface Finishes: Balancing Aesthetics and Protection
Polishing & Buffing
- Result: Mirror‑like sheen; popular for decorative hardware.
- Drawbacks: Shows fingerprints; may require protective coatings.
Galvanizing
- Result: Thick zinc layer for robust corrosion protection.
- Common Uses: Structural steel, fasteners, outdoor equipment.
Powder Coating
- Result: Durable, colorful finish resistant to chipping and UV.
- Applications: Automotive body panels, household appliances.

Black Oxide
- Result: Matte black appearance; minimal dimensional change.
- Applications: Fasteners, firearm components, tool steel parts.
Heat Treatment & Passivation
- Result: Enhanced hardness, toughness, and corrosion resistance.
- Considerations: Must align with material grade and intended service environment.
Best Practices for Designer‑Manufacturer Collaboration
- Share Detailed CAD & GD&T: Include all critical dimensions, surface finishes, and material callouts. Use STEP or IGES files for seamless data transfer.
- Specify Material Standards: Reference ASTM, EN ISO, or JIS grades and supply heat‑treat/annealed conditions.
- Prototype Early: Rapid 3D‑printed or machined steel prototypes validate form and function before full‑scale production.
- Discuss Tolerances: Overly tight tolerances increase cost and lead time; strike a balance between performance and manufacturability.
- Align on Terminology: Ensure common understanding of terms like “cold‑rolled,” “annealed,” “tempered,” and “stainless grades.”
- Establish Feedback Loops: Regular design reviews and on‑site die trials at Toolingsun help catch issues early and refine tooling.
Conclusion: Transform Your Designs with Toolingsun’s Steel Expertise
Steel’s combination of strength, versatility, and sustainability makes it indispensable for product designers across industries. By understanding alloy options, manufacturing processes, and finishing techniques—and by partnering closely with a supplier like Toolingsun—you can deliver robust, cost‑effective products that stand the test of time.
Ready to optimize your steel components? Contact Toolingsun today for a consultation. Let our in‑house metallurgists, design engineers, and manufacturing specialists help you unlock steel’s full potential in your next project.

